Ex: Write a C program to add two matrices using array. How to write a C program to add two matrices using array. C program to add two matrices using array.
Input from user:
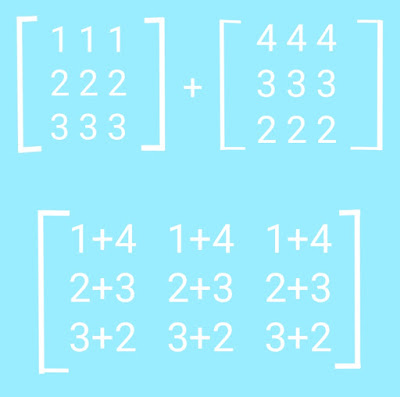
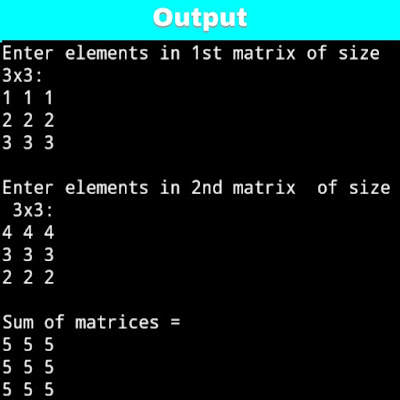
Enter elements in 1st matrix of size 3x3:
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
Enter elements in 2nd matrix of size 3x3:
4 4 4
3 3 3
2 2 2
Expected output:
Sum of matrices=
5 5 5
5 5 5
5 5 5
Matrix addition is done element wise. Means sum of matrices is defined by A+B= A↓ij + B↓ij.
1. Accept two matrices from user declare varible say arr1 and arr2(use 2 dimensional array to store elements).
2. Store elements one by one in arr1 using:
for(row=0;row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr1[row][col]);
}
}
Follow same these steps for arr2.
3. add two matrices arr1+arr2 element wise using:
for(row=0;row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
Input from user:
Enter elements in 1st matrix of size 3x3:
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
Enter elements in 2nd matrix of size 3x3:
4 4 4
3 3 3
2 2 2
Expected output:
Sum of matrices=
5 5 5
5 5 5
5 5 5
- Quick links:
- Logic of matrix addition:
Matrix addition is done element wise. Means sum of matrices is defined by A+B= A↓ij + B↓ij.
Step by Step logic of the given program:
1. Accept two matrices from user declare varible say arr1 and arr2(use 2 dimensional array to store elements).
2. Store elements one by one in arr1 using:
for(row=0;row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr1[row][col]);
}
}
Follow same these steps for arr2.
3. add two matrices arr1+arr2 element wise using:
for(row=0;row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
{
arr3[row][col] = arr1[row][col] + arr2[row][col];
}
}
4. Last print sum of two matrices means resultant matrix arr3.
C program to add two matrices using array:
Above program shows the following output:
arr3[row][col] = arr1[row][col] + arr2[row][col];
}
}
4. Last print sum of two matrices means resultant matrix arr3.
C program to add two matrices using array:
#include<stdio.h>
#define size 3 // size of the matrix
int main()
{
int arr1[size][size]; // 1st matrix
int arr2[size][size]; // 2nd Matrix
int arr3[size][size]; // Resultant matrix
int row, col;
/* input elements in first matrix*/
printf("Enter elements in 1st matrix of size 3x3:\n");
for(row=0;row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr1[row][col]);
}
}
/* input elements in second matrix */
printf("\nEnter elements in 2nd matrix of size 3x3: \n");
for(row=0; row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr2[row][col]);
}
}
/* Add two matrices arr1 and arr2 and store result in matrix arr3*/
for(row=0;row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
#define size 3 // size of the matrix
int main()
{
int arr1[size][size]; // 1st matrix
int arr2[size][size]; // 2nd Matrix
int arr3[size][size]; // Resultant matrix
int row, col;
/* input elements in first matrix*/
printf("Enter elements in 1st matrix of size 3x3:\n");
for(row=0;row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr1[row][col]);
}
}
/* input elements in second matrix */
printf("\nEnter elements in 2nd matrix of size 3x3: \n");
for(row=0; row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr2[row][col]);
}
}
/* Add two matrices arr1 and arr2 and store result in matrix arr3*/
for(row=0;row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0;col<size;col++)
{
arr3[row][col] = arr1[row][col] + arr2[row][col];
}
}
/* Print the value of resultant matrix arr3 */
arr3[row][col] = arr1[row][col] + arr2[row][col];
}
}
/* Print the value of resultant matrix arr3 */
printf("\nSum of matrices = \n");
for(row=0; row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0; col<size;col++)
{
printf("%d ",arr3[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
for(row=0; row<size;row++)
{
for(col=0; col<size;col++)
{
printf("%d ",arr3[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Above program shows the following output: