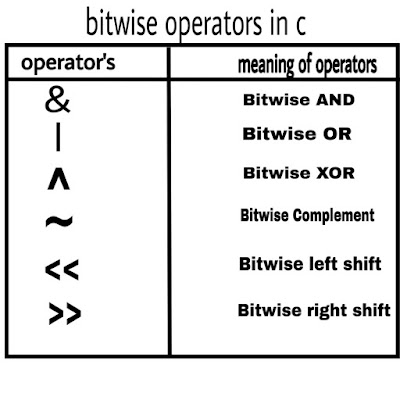
Ex: Write a C program to print Subtraction of given two number. How to print subtraction of given two numbers. C Program to print subtraction of two numbers.
Input from user:
Enter the value of a and b:
50 20
Expected output:
Subtraction is: 30
Step by step logic of the given program:
1. Accept two numbers from user declare variables say a and b.
2.subtract b from a(a-b) and store subtraction in variable c.
3. Print Subtraction on the output screen:
printf("Subtraction is %d",c);
C program to print subtraction of given two numbers :
/***C program to print subtraction of two numbers***/
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b,c;//declear three intiger type variables
//Get input from user
printf("Enter the value of a and b\n");
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
c=a-b;//subract b from a
//display subtraction
printf("Subtraction is %d",c);
}